About Industrial
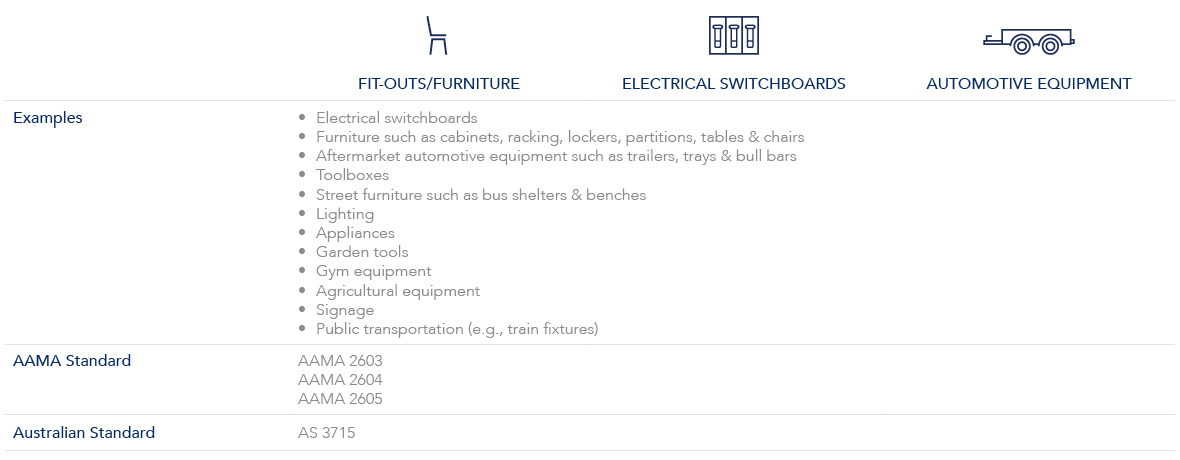
From electrical switchboards and automotive equipment to fitouts, furniture and lighting, Dulux Powder Coatings provide you with the confidence and quality that will make it all worthwhile.
Industrial projects relate to non-architectural items and materials. Examples can be furniture, aftermarket automotive equipment, electrical switchboards, lighting, gym equipment and signage.
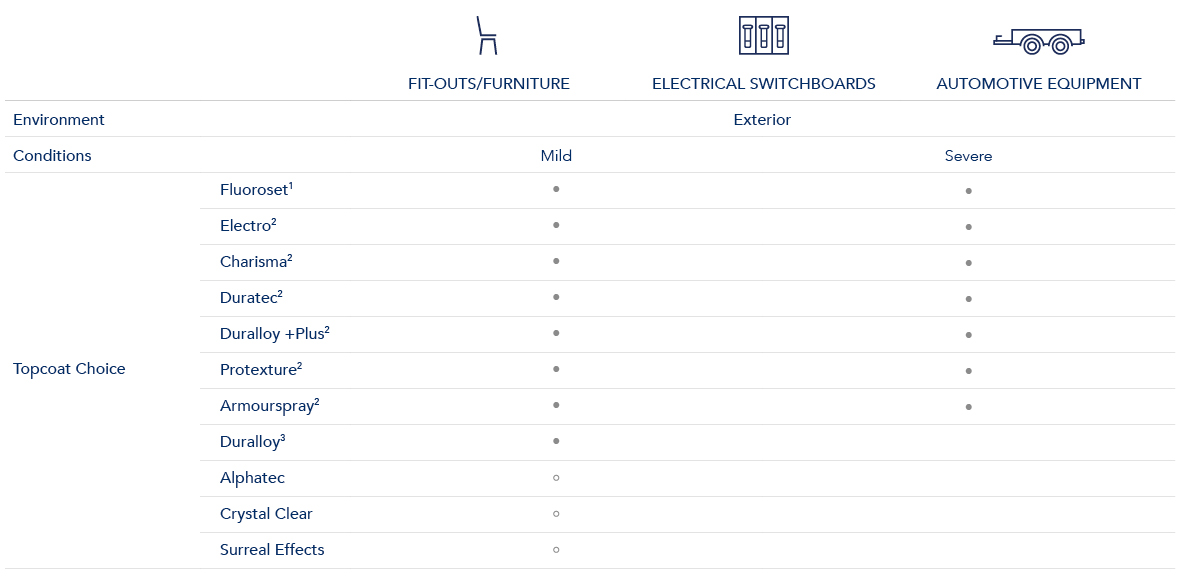
Conditions – Exterior
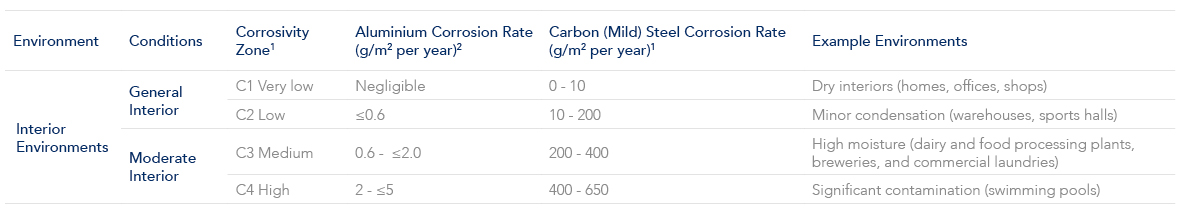
Use the following table which references AS2312.1, SNZTS 3404 and ISO 9223 to identify the environment, conditions and atmospheric corrosivity categories
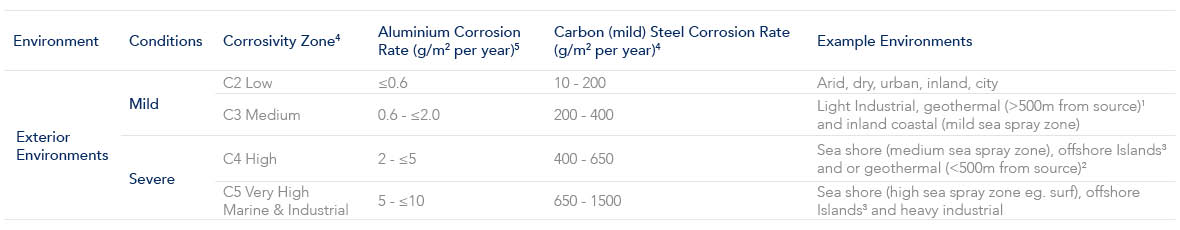
1. Geothermal environments greater than 500m of a bore, mud pool, steam vent, or other source with a pH between 5 and 9. For pH outside this consult Dulux.
2. Geothermal hot spots within 500m of a bore, mud pool, steam vent, or other source.
3. All offshore islands including Waiheke Island, Stewart Island, Fraser Island and Pacific islands eg PNG, Fiji, Samoa, Tonga, Tahiti, Noumea
4. The corrosion rates for the first year of exposure for the different corrosivity categories of Aluminium and Carbon (Mild) Steel are determined by the following standards:
SNZ TS 3404 – Standards NZ Technical Specification – Durability requirements for steel structures & components
AS 2312.1 – Guide to the protection of structural steel against atmospheric corrosion by the use of protective coatings. Part 1: Paint coatings
ISO 9223 – Corrosion of metals and alloys – Corrosivity of atmospheres – Classification, determination and estimation
5. The corrosion rates for the first year of exposure for the different corrosivity categories of Aluminium are determined by the following standard:
ISO 9223 – Corrosion of metals and alloys – Corrosivity of atmospheres – Classification, determination and estimation
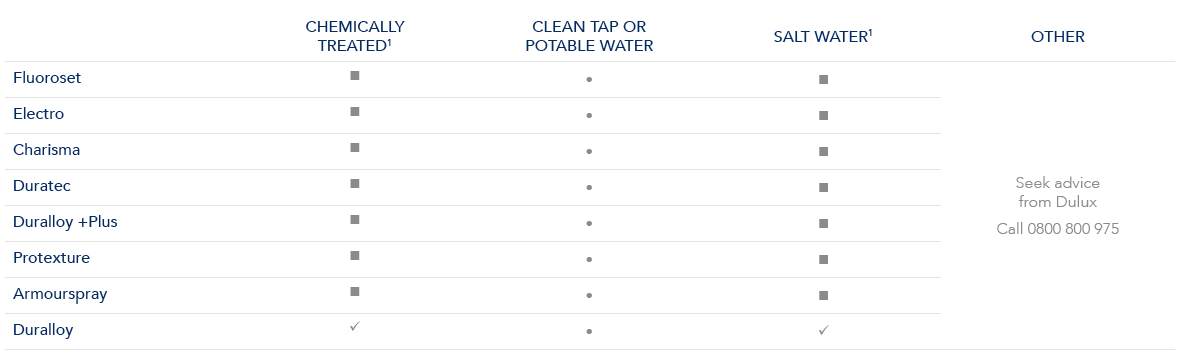
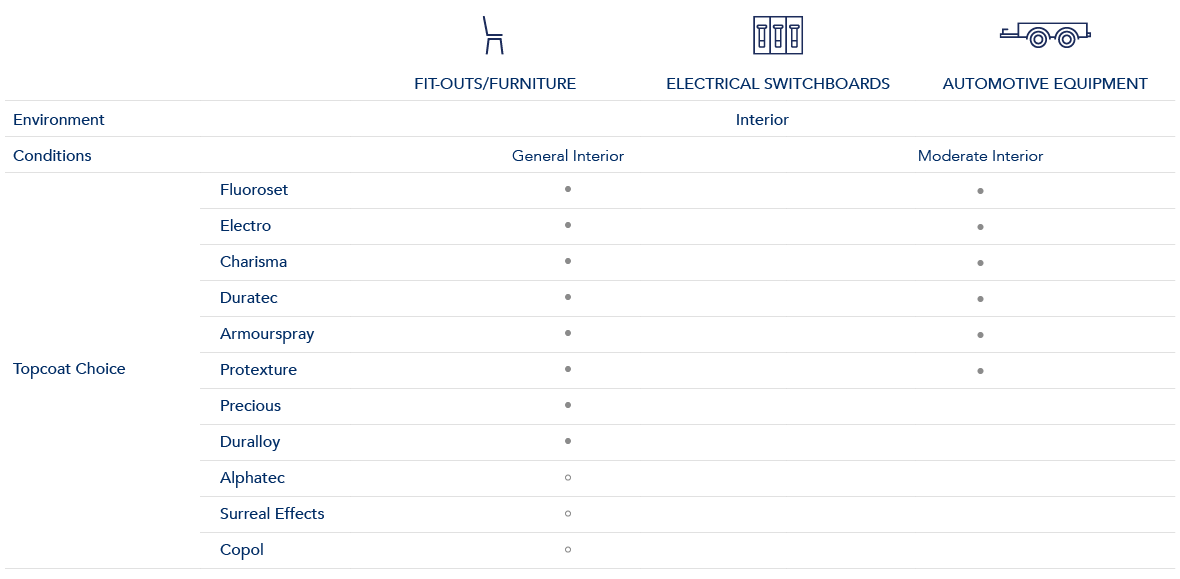
Conditions – interior
Interior environments close to liquids
For any interior application of powder coating on non-habitable projects close to liquids, eg furniture, racking etc please refer to the guidance below for your product options for your project.

1. Aggressive liquids such as Chemically Treated liquids and Salt Water must be cleaned off immediately as per the Dulux Care and Maintenance guide.
Please note chemically treated water includes antimicrobial treatments, e.g. in pools, anti-corrosive chemicals, and soapy water in bathrooms and showers.
■ Where indicated Alumi Shield and Steel Shield warranties are available on areas >than 1m from the liquid.
✓ Where indicated Alumi Shield and Steel Shield warranties are available on areas >than 2m from the liquid (ie outside the splash zone).
● Where indicated Alumi Shield and Steel Shield warranties are available any distance from the liquid.
Alumi Shield and Steel Shield warranties are only available when applied by a Dulux Accredited Powder Coater to the warranty specification on recommended project types and conditions.
All Dulux powder product are NOT suitable in strongly acidic or caustic environments so the pH must be between 5 and 9.
Alumi Shield warranties are not available if the powder coating is immersed in any liquid.